How Are Differences in Properties Among the Transition Elements Explained
I The atomic sizes of the elements of the first transition series are smaller than those of the heavier elements of 2nd and 3rd transition series. The inner transition metals are in the two rows below the body of the table.
Difference Between Transition Metals And Inner Transition Metals Definition Properties In Relation To Electronic Configuration
Why are transition metals different.

. The d -block elements are divided into the first transition series the elements Sc through Cu the second transition series the elements Y through Ag and the third transition. The transition elements are highly denser than the s block elements. The characteristic properties of transition metals include coloured ions complex formation and catalytic activity.
Identify three ways transition metals are separated from their ores. The radii of transition elements stay roughly constant across each row instead of decreasing in size as in the main-group elements. Because the main group elements consist of both metals and nonmetals their physical properties are going to be quite different.
Introduction to General Properties of the Transition Elements. High melting point group 1 metals have low melting points hard group 1 metals are soft high density group 1 metals have lower densities Chemical properties. Most compounds of transition metals are paramagnetic whereas virtually all compounds of the p -block elements are diamagnetic.
The chemical properties of elements are largely determined by the number of valence electrons they contain. The electronegativities of the first-row transition metals increase smoothly from Sc χ 14 to Cu χ 19. The transition elements are in the d-block and in the d-orbital have valence electrons.
Transition metals can form colored compounds. From top to bottom each successive element has a lower ionization energy because it is easier to remove an electron since the atoms are less tightly bound. Similarly from top to bottom elements decrease in electronegativity due to an increasing distance.
The magnetic moment of the transition element or ion is determined by the number of unpaired electrons and is calculated by using the spin-only magnetic moment formula. There is a relatively low gap in energy between the possible oxidation states of these elements. 5 metals are now red to transition metals and th oxophilic an of d e elements explain their affinity toward hard bridging ligands the formation of m l bonds is difficult for these elem O h drocarbons.
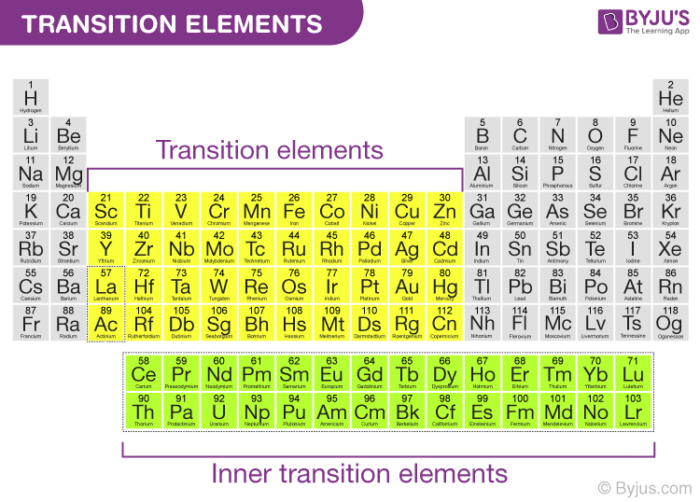
A transition metal is a chemical element that has a partially filled d orbital. Transition metals are less reactive compared to other metals. They are the Lanthanides and the Actinides.
The physical and chemical properties of transition elements differ from the main group elements s-block. They have a high chargeradius ratio. Compared to other metals most transition metals have.
These elements form coloured compounds and ions. The density and hardness of transition elements are high due to the small size of their atoms and the strong metallic bonding. They are frequently paramagnetic.
Explain how a metal can become a temporary magnet. Transition metals can have various oxidation states within compounds but other metals can have limited number of. Their properties are periodic because the number of valence electrons is periodic.
Are isotopes different in. However the atom sizes of the elements in the third transition series are virtually the same as those of. The transition metals are located in groups 311 of the periodic table.
Thus Sc is a rather active metal whereas Cu is much less reactive. The magnetic properties of the d-block elements are determined by the number of unpaired electrons present in them. They can form several states of oxidation and contain different ions.
Properties of Transition Elements The transition elements general properties are as follows. How are differences in properties among the transition elements explained. A covalent bond in which both electrons are donate by one atom.
Inner transition elements are in the f-block and in the f-orbital have valence electrons. This colour is explained by the d-d transition of electrons. High density and hardness.
The elements with incompletely filled d-subshell in their ground state or most stable oxidation state are named as D-block elementsThey are additionally named as transition elementsThe partially filled subshells incorporate the n-1 d subshellAll the d-block elements have a similar number of electrons in. In the periodic table of. Scandium and zinc are both in the d-block but they are not transition metals.
They are typically metals with a high melting point. Quick Summary of the Transition Metal Properties Low ionization energies Positive oxidation states Multiple oxidation states since there is a low energy gap between them Very hard Exhibit metallic luster High melting points High boiling points High electrical conductivity High thermal conductivity Malleable. The difference is.
They have a variety of oxidation states. Theyre excellent conductors of electricity. What is the properties of transition elements.
Some properties of transition elements are different from those of the metals in group 1. Properties of transition elements are discussed below. These properties of the transition elements are listed below.
Late transition metals in the g ft and have a high affinity toward sulfur or selenium. Densities and Metallic Radii. They have to properties of metals.
The transition elements therefore exhibit many oxidation states. The properties of the elements of the first transition series differ from those of the heavier transition elements in many ways. They usually combine to form coloured compounds.
For example elements on the left in groups 1 2 and 13 are going. The pattern of the ionic radius is. Explain why some metals can act as permanent magnets.
Describe the characteristic properties of transition metals. How can a transition metal form an ion with a charge of 3 or higher. Their densities gradually decrease from scandium to copper because of an irregular decrease in metallic radii and a relative increase in atomic mass.
The three main differences are. The key difference between first second and third transition series is that the outermost d orbital of first transition series elements is 3d while the outermost d orbital second transition series is 4d and the outermost d orbital in third transition series is 5d.
Transition Elements General Properties And Trends With Faqs

Science Review Of Transition Metals Free Homework Help

Transition Metals Elements Definition List Properties Transition Metal Electron Configuration Ionization Energy
No comments for "How Are Differences in Properties Among the Transition Elements Explained"
Post a Comment